Case Discussion – 1
DIAGNOSIS – GDM ON MEAL PLAN WITH FETAL CARDIAC DEFECTS
26 yrs – Primi/ Mrs. R 25/F, accountant by occupation , booked elsewhere , LMP-10/02/2020, EDD – 17/11 2020/ First visit to SNS Hospital on 07/10/2020 @ 35 weeks. Known case of GDM on Meal plan since three months of pregnancy / she was under vigilant monitoring of blood glucose , maternal wt gain, Bp, monitoring throughout the pregnancy.
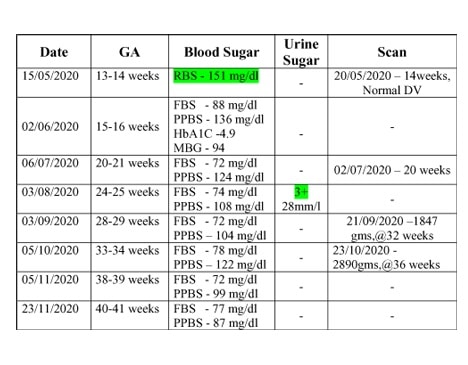
The plasma Glucose levels seems apparently well under control.
Her serial growth scans showed EFW – <50th percentile.
Underwent cesarean delivery on -18/11/2020 for Dystocia of Labour, and delivered Girl – 4.00 kg. Early neonatal and postnatal period uneventful. No episodes of hypoglycemia in the baby. Maternal Blood glucose within normal limits.
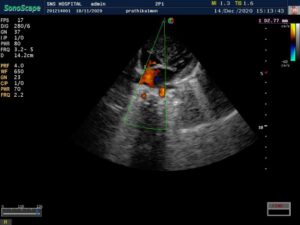
CARDIAC screening of the baby was done – is fourth week of life. Showed –
> Acyanotic congenital heart disease.
VSD – 5mm – muscular non –
restrictive.
ASD – 4mm – L-R shunt
PDA – 2.5mm – L-R shunt. Baby underwent corrective surgery and is thriving well.
Points to ponder – Doctors` corner:
Even one marginally higher blood glucose – (151mg/dl – 13weeks) in the earlier trimester -though we name it as GDM – Should, arouse a suspicion of embryonic defects.
All the parameters were apparently under control throughout pregnancy, with meal plan – yet the Fetus had undergone the insult at the very earliest stage – should we redefine the terminology – GDM?
How far does the meal plan take care of the Intra uterine fetus – is Questionable.
Defining any single abnormal blood glucose values as diabetesmelitus complicating pregnancy – like what has been done in this case helps us to keep a close watch.
Asian ethnicity being a high risk for Diabetes complicating pregnancy – we see a tremendous increase in the incidence of number of pregnancies complicated with Diabetes.
Strict monitoring and control of blood glucose helps us prevent late intra uterine complications (sudden fetal death) intrapartum and early neonatal complications, not reliable is preventing embryonic insults though. Which says the pathogenesis of congenital abnormalities seen in babies born to diabetic mothers might be because of cytopathic effect of maternal immune system.
Case Discussion – 2
DIAGNOSIS – GDM ON INSULIN
30 yrs, Primi / Dentist by occupation/ EDD-26/11/2020. Booked at Bangalore / her first visit to our hospital @ 32 weeks.
Was diagnosed GDM at 32 weeks when RBS was 161 mg/dl. Was started on metformin patient was allergic to metformin, started on insulin.

At term EFW 3.4-3.5kg. Head was just fixed not engaged, admitted with labour on 16/11/2020, progress of labour and blood glucose levels, fetal heart rate pattern closely monitored.
Patient delivered on 17/11/2020 by Instrument assisted vaginal delivery. Birth weight 3.75kgs, cord around neck, postnatally maternal blood glucose monitored. Baby monitored for hypoglycemia physiological jaundice.
Early neonatal ultrasound cranium and fetal echo performed – was found within normal limits




Discussion – Doctors` corner:
Medicine carries the pride of saying “every patient is different from the other, every case we see teaches us something “
According to the table, she should have been diagnosed diabetic at 20 weeks. The blood glucose, has been apparently normal on several occasions of repeat testing.
The fluctuation in blood glucose levels throughout pregnancy has not been drastic even during the period of maximum insulin resistance and therefore the perinatal complications as well.
This might give us the assumption that the ease of glucose control, the necessity, dosage and duration of insulin requirements might be directly proportional to the intrapartum and perinatal complications. This has been well cited in textbooks.
Insulin appears to be a better option in GDM diagnosed in late trimester, more effective in preventing macrosomia.
We do see a degree of reluctance and hesitancy in accepting the diagnosis of GDM among pregnant women.
Case Discussion – 3
DIAGNOSIS – TYPE 2 DM ON INSULIN WITH INTRA UTERINE GROWTH RESTRICTION
32 yrs, MRS. M, G3P1L1A1 / LMP -03-06-2020 / EDD – 10-03-2021/ previous intrauterine growth restriction with a birth wt of 1.75kg.
Seen first time @ 18 weeks gestation in the month of October.




First visit U/s – 2+, hence was advised GTT., FBS-101 mg/dl, 1hour-206 mg/dl, 2hours-201mg/dl, patient started on INSULIN 5Iu-5Iu
The insulin requirement kept changing as the pregnancy advanced .she was already on aspirin and her uterine Doppler showed low resistance flow. Growth scan with Doppler every 4weeks done from 20 weeks.
There was growth lag of 2weeks @ 27 weeks gestation, Doppler U/A 50th percentile followed by growth scan every 2weeks with Doppler.
The parameters fell below 50th percentile but the interval growth was satisfactory.
Steroids completed @ 33weeks patient had PPROM @ 35 weeks, and delivered an alive preterm vaginal delivery – Boy, 2.2kg.
Postnatally baby had recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia for 72 hours after delivery. Physiological jaundice on D3 was put on phototherapy, Baby and mother were discharged on day 5.
Mother switched to OHA. Baby echo fixed on 13/03/2021, awaited.
Gestational Diabetes melitus – Information – Patients corner:
1. What is Gestational Dm?
Abnormally high blood glucose values occurring or deducted for the first time in pregnancy is called.
2. Why is this GDM important to be diagnosed?
GDM if not Diagnosed and treated properly will lead to serious implications of the fetus inside the uterus – as well as on the baby soon after birth. Complications like Heart (cardiac) problems, skeletal (bones & muscles) problems, Jaundice and Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) after birth.
3. Can all the complications be prevented?
Certain Fetal effects of diabetes can be suspected and detected at earlier stage, not all complications are detectable and preventable. Neonatal (New born) complications are preventable and treatable.
4. Who are at risk of GDM?
Asian ethnicity (Indians) / previous H/o GDM in (previous Pregnancy) / H/o big babies is previous pregnancy / Family H/o DM (Diabetes in parents) etc.
5. How do we detect (find out) GDM?
Screening for GDM is carried out is all pregnant women during first three months, 5th month of pregnancy and is Last Trimester by Glucose Challenge test.
6. What is the treatment for GDM?
Maternal Blood Glucose levels can be kept under control by medications , diet plans and exercise and insulin . many women might require insulin for a better control of blood glucose .Recently no prick self monitoring blood glucometers are available which makes us monitor blood glucose levels throughout the day.
Preferably: – FBS – 95.4 mg/dl
Post prandial 1 hour – 140.4 mg/dl
2 hour – 115.2 mg/dl
7. What is the difference between type 2 diabetes and GDM?
TYPE 2 DM is diabetes that has occurred before pregnancy. GDM is the one which occurred or detected for the first time during pregnancy. The management of each case is different because type 2 diabetes monitoring requires checking for end organ (kidney, eyes) damages, and fetal congenital anomalies.
General advice to woman with GDM/ who had GDM during their pregnancies
Women with GDM – should have their blood glucose checked every day as per doctors advice.
Women with GDM should not be reluctant – to have SMBG device. Installed – self monitoring of blood glucose device – which allows – to monitor 24 hrs Blood Glucose without needle pricks and can be tracked in mobile apps.
Women with H/o GDM in one pregnancy is prone to get GDM is next pregnancy and is prone to have Diabetes is future , So regular exercise and lifestyle modifications is must to postpone Diabetes in later life .